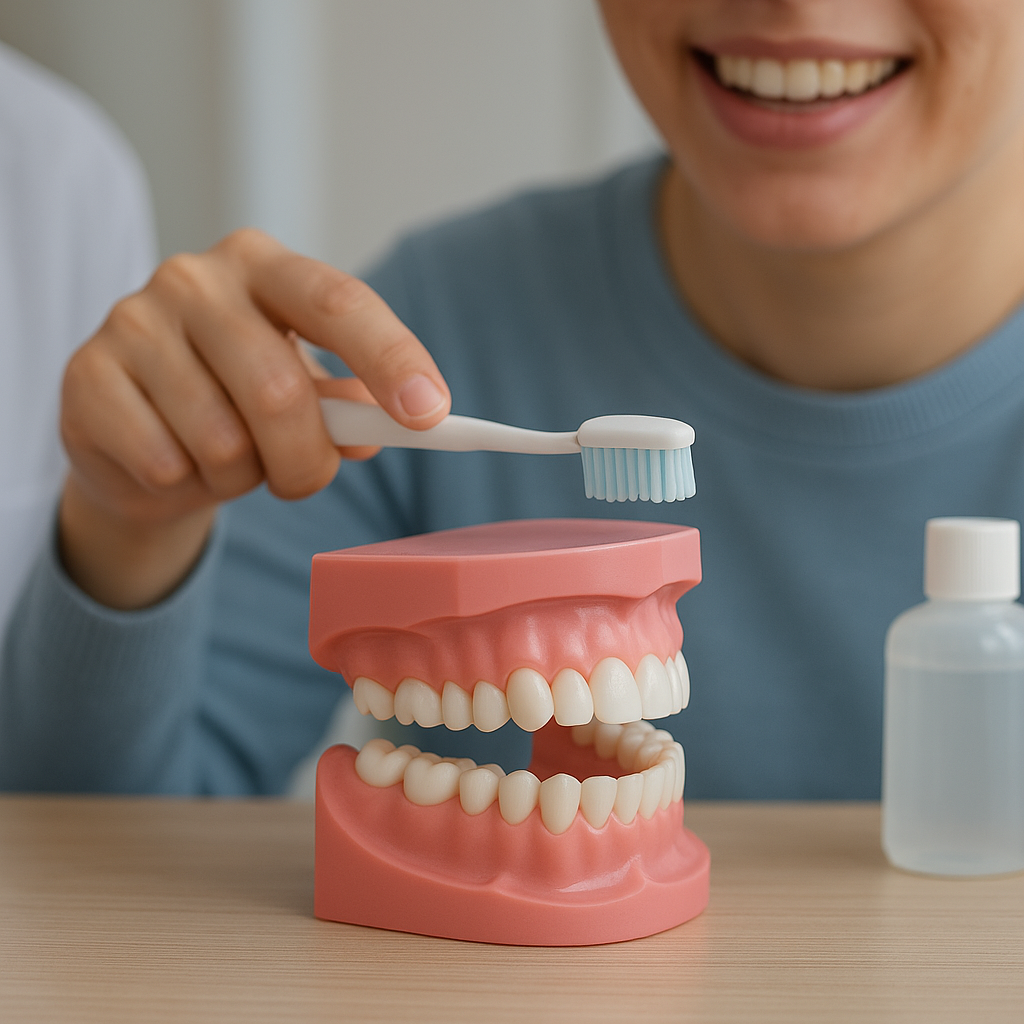
The role of dental hygienists in patient education is crucial for promoting oral health and preventing dental diseases. These professionals serve as the frontline educators in dental practices, providing patients with the knowledge and tools necessary to maintain optimal oral hygiene. Their expertise not only enhances the patient experience but also contributes significantly to the overall effectiveness of dental care. This article will explore the various responsibilities of dental hygienists in patient education, the techniques they employ, and the impact of their work on patient outcomes.
Understanding the Role of Dental Hygienists
Dental hygienists are licensed professionals who specialize in preventive oral health care. Their primary responsibilities include performing dental cleanings, taking X-rays, and conducting assessments of patients’ oral health. However, one of their most vital roles is educating patients about proper oral hygiene practices. This education encompasses a wide range of topics, including brushing and flossing techniques, dietary choices, and the importance of regular dental visits.
Patient Assessments and Individualized Education
Before providing education, dental hygienists conduct thorough assessments of each patient’s oral health. This process involves examining the gums, teeth, and overall oral cavity to identify any issues such as plaque buildup, gum disease, or cavities. Based on these assessments, hygienists can tailor their educational approach to meet the specific needs of each patient.
- Identifying Risk Factors: During assessments, hygienists identify risk factors that may contribute to poor oral health, such as smoking, diabetes, or a high-sugar diet. Understanding these factors allows them to provide targeted advice.
- Creating Personalized Care Plans: Hygienists often develop individualized care plans that outline specific oral hygiene practices and recommendations for each patient. This personalized approach enhances the effectiveness of their education.
Effective Communication Techniques
Effective communication is essential for dental hygienists when educating patients. They must convey complex information in a way that is easily understandable. This often involves using simple language, visual aids, and demonstrations. For instance, hygienists may use models of teeth to show proper brushing techniques or provide pamphlets that summarize key points discussed during the appointment.
- Visual Aids: Utilizing diagrams, videos, and models can help patients grasp the importance of oral hygiene practices. Visual aids make the information more relatable and easier to remember.
- Demonstrations: Hygienists often demonstrate proper brushing and flossing techniques during appointments. This hands-on approach allows patients to practice these skills under professional guidance.
The Impact of Patient Education on Oral Health
The education provided by dental hygienists has a profound impact on patients’ oral health outcomes. Research has shown that patients who receive thorough education about oral hygiene are more likely to adopt healthier habits, leading to improved dental health. This section will explore the various ways in which patient education influences oral health.
Improved Oral Hygiene Practices
One of the most significant outcomes of effective patient education is the improvement in oral hygiene practices. When patients understand the importance of regular brushing and flossing, they are more likely to incorporate these practices into their daily routines. Dental hygienists play a pivotal role in reinforcing these habits.
- Increased Compliance: Patients who receive education about the consequences of neglecting oral hygiene are more likely to comply with recommended practices. This compliance can lead to a decrease in the incidence of cavities and gum disease.
- Long-Term Behavior Change: Education provided by hygienists can lead to long-term behavior changes. Patients who understand the link between oral health and overall health are more motivated to maintain their oral hygiene.
Reduction in Dental Issues
Another significant impact of patient education is the reduction in dental issues. By equipping patients with the knowledge to care for their teeth and gums, dental hygienists help prevent common problems such as cavities, gingivitis, and periodontal disease.
- Preventive Care: Educated patients are more likely to seek preventive care, such as regular cleanings and check-ups. This proactive approach can catch potential issues before they escalate into more serious problems.
- Cost Savings: By preventing dental issues through education, patients can save money on more extensive treatments in the future. This financial incentive further encourages adherence to recommended oral hygiene practices.
Challenges Faced by Dental Hygienists in Patient Education
Despite the critical role dental hygienists play in patient education, they face several challenges that can hinder their effectiveness. Understanding these challenges is essential for improving educational strategies and enhancing patient outcomes.
Time Constraints
One of the primary challenges dental hygienists encounter is time constraints during appointments. With a busy schedule, hygienists may have limited time to spend with each patient, making it difficult to provide comprehensive education.
- Balancing Care and Education: Hygienists must balance the need to perform clinical tasks with the desire to educate patients. This balancing act can lead to rushed appointments, where education may take a backseat.
- Prioritizing Key Messages: To maximize the limited time available, hygienists often need to prioritize key messages. This can result in some important information being overlooked.
Patient Engagement and Motivation
Another challenge is engaging patients and motivating them to take an active role in their oral health. Some patients may be indifferent or resistant to education, making it difficult for hygienists to instill the importance of proper oral hygiene.
- Overcoming Resistance: Hygienists must develop strategies to overcome patient resistance. This may involve building rapport, understanding patients’ concerns, and addressing any misconceptions they may have about oral health.
- Encouraging Active Participation: Encouraging patients to ask questions and participate in their care can enhance their understanding and commitment to oral hygiene practices.
Future Directions in Patient Education by Dental Hygienists
As the field of dentistry continues to evolve, so too does the role of dental hygienists in patient education. Emerging technologies and innovative approaches are shaping the future of how hygienists educate their patients.
Utilization of Technology
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in patient education. Dental hygienists are beginning to leverage digital tools to enhance their educational efforts.
- Telehealth: The rise of telehealth has opened new avenues for patient education. Hygienists can conduct virtual consultations, providing education and support to patients in a convenient format.
- Mobile Apps: Many dental practices are adopting mobile apps that provide patients with reminders, educational resources, and tracking tools for their oral hygiene routines.
Community Outreach and Public Health Initiatives
In addition to individual patient education, dental hygienists are increasingly involved in community outreach and public health initiatives. These efforts aim to raise awareness about oral health on a larger scale.
- School Programs: Many hygienists participate in school programs that educate children about the importance of oral hygiene. These early interventions can instill healthy habits from a young age.
- Public Health Campaigns: Hygienists often collaborate with public health organizations to promote oral health awareness through campaigns, workshops, and community events.
In conclusion, dental hygienists play a vital role in patient education, significantly impacting oral health outcomes. Through personalized assessments, effective communication, and innovative approaches, they empower patients to take charge of their oral hygiene. Despite facing challenges such as time constraints and patient engagement, the future of patient education in dentistry looks promising, with technology and community outreach paving the way for improved oral health awareness. As the field continues to evolve, the contributions of dental hygienists will remain essential in fostering a culture of preventive care and lifelong oral health.