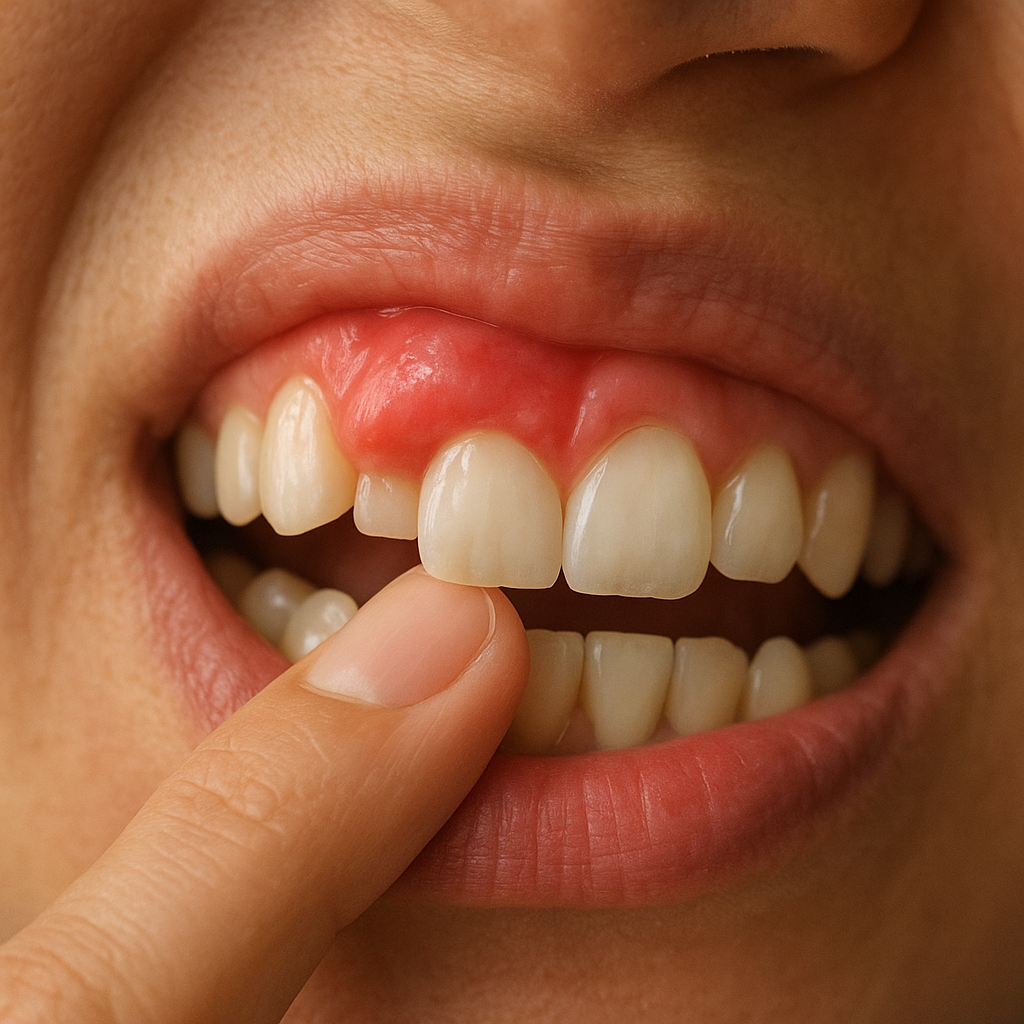
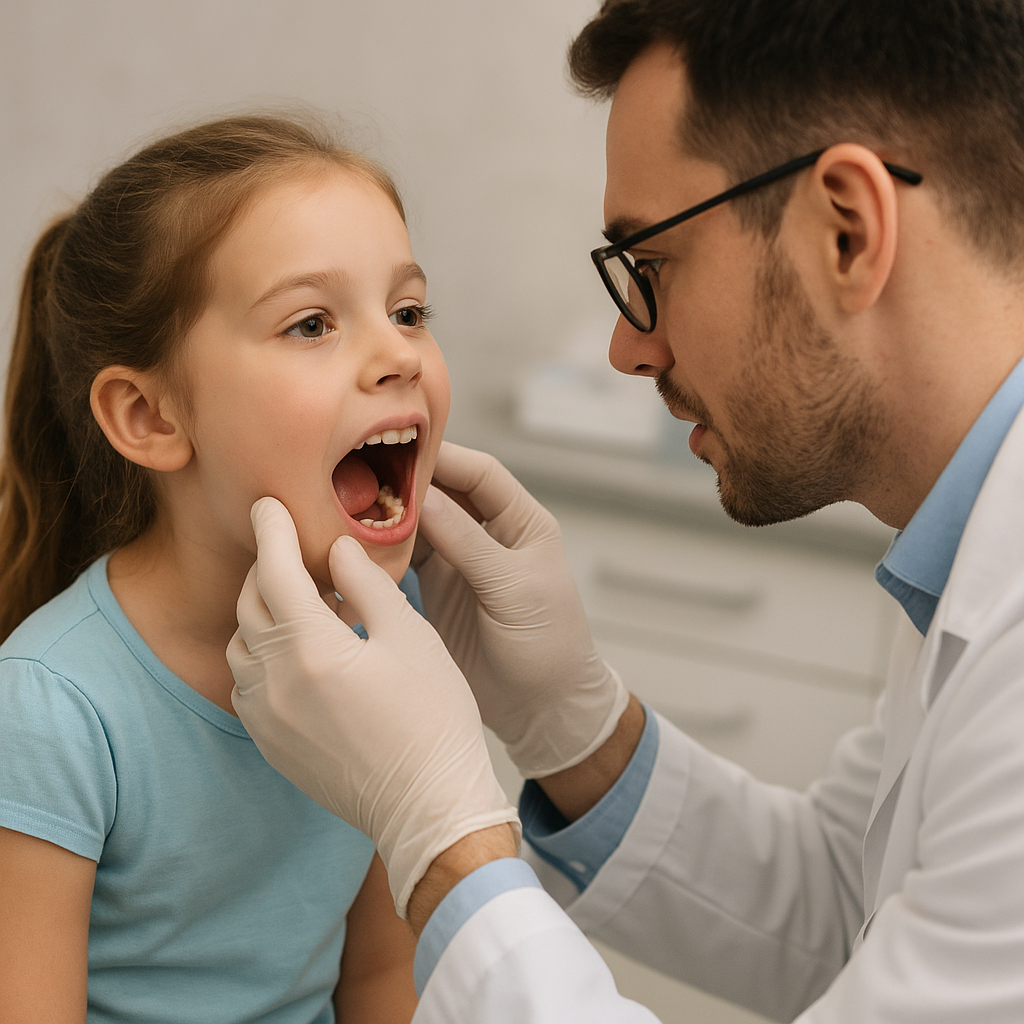
Swollen gums can be both uncomfortable and alarming. Understanding why this happens and how to address it promptly is essential for maintaining optimal oral health. This article explores various aspects of gum swelling, from common causes and home remedies to professional treatments and preventive strategies.
Understanding the Common Causes
Several factors can contribute to gum swelling. Identifying the underlying reason is the first step toward effective treatment and relief.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Neglecting regular brushing and flossing allows plaque to build up along the gumline. Over time, this bacterial film irritates the gums, leading to inflammation and swelling.
Gingivitis and Periodontitis
Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, marked by redness, bleeding, and mild swelling. If left untreated, it can progress to periodontitis, where deeper tissues and bone supporting the teeth become infected.
Hormonal Fluctuations
Changes in hormone levels during puberty, pregnancy, menstrual cycles, or menopause can increase blood flow to the gums, making them more sensitive and prone to swelling.
Medication Side Effects
Certain medications, such as anticonvulsants, immunosuppressants, and some heart drugs, can cause gum overgrowth or swelling as an adverse effect.
Vitamin Deficiencies
A deficiency in essential nutrients—particularly vitamin C and some B vitamins—can impair gum health, weakening tissue and causing inflammation.
Effective Home Remedies
For mild gum swelling, simple remedies can provide quick relief and reduce discomfort. Always consult a dentist if symptoms persist.
- Saltwater Rinse: Dissolve half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water. Swish gently around your mouth for 30 seconds, then spit. Repeat twice daily to reduce bacteria and soothe gums.
- Cold Compress: Apply a cold pack or an ice cube wrapped in cloth to the outside of your cheek for 10–15 minutes. This helps alleviate pain and minimize swelling.
- Hydrogen Peroxide Rinse: Mix equal parts 3% hydrogen peroxide and water. Swish for 30 seconds, then rinse with plain water. This disinfects the area and decreases bacteria.
- Chamomile Tea: Brew a cup of chamomile tea, let it cool, then use it as a mouth rinse. Chamomile contains anti-inflammatory properties that can calm irritated gums.
- Oil Pulling: Swish a tablespoon of coconut or sesame oil in your mouth for 10–15 minutes. This ancient practice may reduce plaque and promote gum health.
These methods can be repeated daily until the swelling diminishes. However, they are not substitutes for professional care when needed.
When to Seek Professional Help
Persistent or severe gum swelling warrants a visit to a qualified dentist. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent more serious complications.
Signs You Need Immediate Attention
- Intense pain or throbbing in the gums
- Visible pus or discharge around teeth
- Loose teeth or shifting bite
- Fever or general malaise
- Gums receding significantly
Diagnostic Procedures
Your dentist may perform a thorough exam, including:
- Dental X-rays to assess bone loss
- Periodontal probing to measure pocket depths
- Microbial tests to identify specific bacteria
Based on findings, treatment plans can range from deep cleaning (scaling and root planing) to more advanced therapies for severe periodontitis.
Advanced Dental Treatments
When home care and basic procedures are insufficient, these professional interventions may be recommended:
- Scaling and Root Planing: A deep cleaning technique to remove tartar and bacteria below the gumline.
- Antibiotic Therapy: Topical or oral antibiotics to eliminate infection.
- Laser Gum Treatment: Minimally invasive option to reduce bacteria and promote healing.
- Gum Grafting: Surgical procedure to restore receding gums and improve aesthetics.
- Regenerative Procedures: Use of grafting materials or growth factors to regenerate bone and tissue.
Preventive Measures for Healthy Gums
Prevention is the most effective strategy to avoid swollen gums. Incorporate these habits into your daily routine:
- Brush at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste
- Floss daily to remove interdental plaque
- Use an antibacterial mouthwash to reduce microbial load
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals
- Stay hydrated to support salivary flow
- Schedule regular dental checkups and cleanings every six months
By following these guidelines, you can significantly lower the risk of gum swelling and maintain a healthy, confident smile.