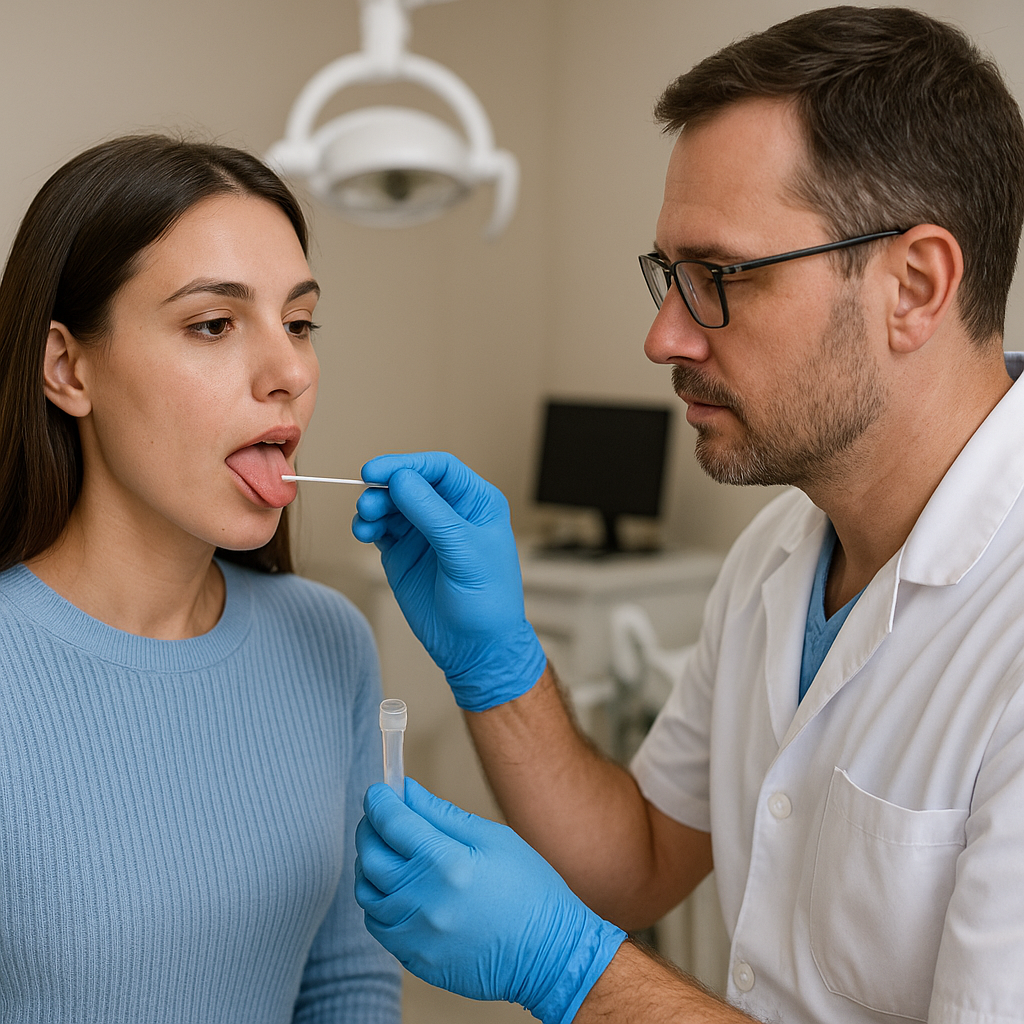
The emergence of saliva testing as an innovative diagnostic tool is rewriting the narrative of modern dental practice. By harnessing the power of biomarkers found in oral fluids, clinicians can detect disease, assess risk, and tailor treatment plans with unprecedented accuracy. This non-invasive approach is rapidly gaining traction among dentists, researchers, and patients alike, offering a compelling alternative to traditional blood tests and radiographic imaging techniques. As advances in molecular biology and sensor technology converge, saliva-based diagnostics promise to become an indispensable component of comprehensive oral health care.
The Science Behind Saliva Diagnostics
Saliva, often dismissed as a mere digestive fluid, is in fact a rich biological medium containing a vast array of molecular constituents. From enzymes and hormones to antibodies and genetic material, each component offers unique insights into both oral and systemic conditions. Key elements of this scientific revolution include:
- Proteomic profiling – Identifying and quantifying proteins that reflect inflammatory states, tissue degradation, or healing processes within the oral cavity.
- Genomic analysis – Detecting microbial DNA to map the microbial communities responsible for caries, periodontal disease, and opportunistic infections.
- Transcriptomics – Measuring RNA transcripts that reveal gene expression patterns associated with cancer, autoimmune disorders, and metabolic imbalances.
- Metabolomics – Monitoring small molecules produced by host and bacterial metabolism, which can indicate oxidative stress, nutritional deficiencies, and systemic diseases like diabetes.
- Immunoassays – Quantifying antibodies or inflammatory markers such as C-reactive protein (CRP) to evaluate infection status and healing potential.
Through sophisticated analytics platforms, these data streams are integrated to provide a holistic view of patient health. Algorithms and machine learning models further enhance predictive accuracy, enabling clinicians to move from reactive treatment to proactive prevention.
Clinical Advantages Over Traditional Methods
Traditional dental diagnostics rely heavily on visual examinations, radiographs, and invasive sampling techniques. While effective to a degree, these methods have limitations related to patient comfort, diagnostic sensitivity, and real-time monitoring. Saliva testing addresses these challenges by offering:
- Non-invasive sample collection – Eliminating needle anxiety and minimizing patient discomfort, which fosters higher compliance, especially in pediatrics and geriatrics.
- Rapid chairside results – Many point-of-care devices deliver actionable data within minutes, streamlining workflow and enabling immediate clinical decision-making.
- Enhanced sensitivity and specificity – Molecular assays can detect disease markers at very low concentrations, identifying early-stage pathology that might be missed by imaging alone.
- Cost-effectiveness – Reducing reliance on expensive lab-based tests and cutting down on chair time translates to both practice profitability and patient affordability.
- Longitudinal monitoring – Easy repeat sampling allows tracking of disease progression and treatment response over time without radiation exposure.
By integrating saliva diagnostics into routine check-ups, dental professionals can identify at-risk individuals and intervene promptly. For example, monitoring levels of Streptococcus mutans DNA can help predict caries risk, while salivary cortisol measurements may flag patients under stress, who are more prone to conditions like bruxism and periodontitis.
Implementation in Modern Dental Practices
Transitioning from concept to clinical reality requires thoughtful implementation strategies. Dentists and practice managers should consider the following steps:
- Equipment and training – Investing in point-of-care devices or establishing partnerships with specialized laboratories. Training staff on proper sample collection, handling protocols, and data interpretation is essential.
- Workflow integration – Incorporating saliva testing into standard appointment templates. For instance, designating specific time slots for sample collection at the start of check-ups avoids disruptions.
- Patient education – Explaining the benefits of saliva diagnostics helps build trust and encourages patient participation. Visual aids and informational brochures can clarify how this technology enhances personalized care.
- Data management and privacy – Ensuring secure storage and compliance with healthcare data regulations. Integrating diagnostic results into electronic health records (EHR) promotes continuity of care across medical disciplines.
- Insurance and billing – Navigating reimbursement codes and advocating for coverage. Demonstrating the long-term cost savings from early disease detection can support policy changes.
Successful adopters report not only improved clinical outcomes but also increased patient satisfaction. Many individuals appreciate the personalized nature of tailored preventive plans and the reassurance provided by objective health metrics. In turn, this fosters stronger patient–dentist relationships and loyalty.
Future Directions and Challenges
Despite its promise, saliva testing faces hurdles before it can become a universal standard. Key areas for future development include:
- Standardization of protocols – Harmonizing collection methods, storage conditions, and assay parameters to ensure reproducibility across practices and studies.
- Regulatory approval – Navigating the complex landscape of medical device and diagnostic regulations to secure clearance for new tests.
- Technological miniaturization – Refining sensor platforms for more compact, user-friendly devices that can be seamlessly incorporated into dental operatories.
- Expanded biomarker discovery – Ongoing research to identify novel indicators for oral cancer, systemic diseases, and even genetic predispositions to certain conditions.
- Interdisciplinary collaboration – Bridging gaps between dental, medical, and research communities to foster holistic patient management.
Addressing these challenges will require sustained investment in research and education. However, the potential rewards are substantial: a future in which chairside saliva analysis empowers dentists to detect disease earlier, tailor interventions more accurately, and ultimately, improve overall patient health. As the field advances, we will witness a paradigm shift from isolated symptom management to integrated, data-driven diagnostics that span the continuum of care.
Embracing a New Era of Preventive Dentistry
By championing saliva testing, dental professionals have an opportunity to elevate the standard of care. This innovative approach not only enhances diagnostic precision but also fosters a deeper understanding of the intricate interplay between oral and systemic health. As patients become more informed and demanding of personalized solutions, implementing saliva-based diagnostics will distinguish forward-thinking practices and redefine success in modern dentistry.